How To Teach Kids To Draw People

Here is a brief overview of the fascinating stages of cartoon in child development and why it'southward important to encourage young children to depict.
Drawing is a natural process for all children. From infancy, children begin by experimenting with drawing tools and making marks on paper, and every bit they grow, these marks first taking on pregnant.
Drawing ultimately becomes a child's way of expressing their understanding of the world and all the things that are important to them.
Find out how children learn to draw and why it's a crucial activity. There is also a breakdown of the stages of drawing development at various ages.
How to Teach a Child to Draw
During the early years, Information technology'southward important to focus on the process of creative drawing, and not on the product.
There is no need to formally teach children to draw. The best way to teach them is to give them exposure to materials and drawing tools and let them express themselves freely.
Equally they grow and mature, their drawings will become more detailed and reflect the world effectually them.
Avoid the temptation to provide models for children to copy and limit their exposure to colouring books . These only serve to take away natural inventiveness.

Why Drawing is Important
There are many benefits of drawing during the toddler and preschool years. Information technology:
- builds a child'south fine motor skills
- develops hand-eye coordination
- develops creative expression through complimentary cartoon
- is the foundation of pre-writing skills
- builds a child'due south attention bridge
- develops cognitive understanding of concepts
Tracing pictures or "teaching" a child to describe by following models are not natural, age-appropriate ways to develop creativity.
The Stages of Drawing
Hither are the characteristics of the diverse developmental stages of children's drawings. These are not set in rock equally children develop at their own unique rates.
They will attain the milestones at their own step, however, they all progress through the same stages, which are based on their level of agreement.
The characteristics are listed by age.
Watch the video below for a summary of each stage, or read on for a breakdown of the diverse ages.
12 Months: Random Marks and Scribbles
The first stage of cartoon is most exploring and developing motor coordination.
At effectually 15 to 18 months babies begin to develop uncontrolled scribbles that don't stand for anything.
Shapes
Babies begin by making random marks and before long brainstorm to form:
- scribbles
- vertical and horizontal lines
- multiple line drawings
Understanding
For babies, drawing is really well-nigh learning crusade and effect and their ability to brand things happen.
It has footling to exercise with creating and representing their world, and more to practice with enjoying their movements and the effects of them.
Their scribbles enable them to learn about the properties of objects, materials and tools such as pencils, pens, paint, crayons and paper.
Grip
From around 15 months of age, toddlers are ordinarily able to grasp crayons with their whole mitt (called a palmar grasp).
ii Years: Controlled Scribbles
This stage is known every bit controlled scribbling .
It is characterized by spontaneous circular or to-and-fro scribbles and dots.
Similar scribbles tin be found in all children's drawings at this age and the shapes in them are necessary for developing drawing and writing skills subsequently.
Shapes
Toddlers begin to brand drawings that include:
- horizontal and vertical lines
- multiple loops and spirals
- roughly drawn circles
- shapes that resemble messages T and V
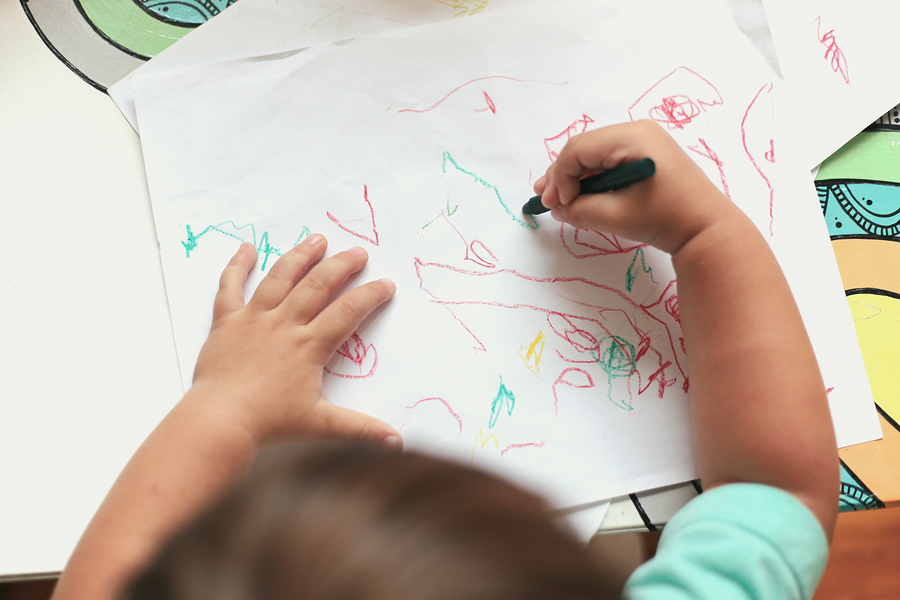

Grip
Ii-year-olds larn to concord a pencil well down the shaft towards the point, using their pollex and first ii fingers (called a tripod grasp).
They volition usually use their preferred hand.
Understanding
At this age, toddlers begin to discover the connection between the movements they make and the marks that form on the paper. They will begin to repeat movements on purpose.
Past the end of this year, these drawings evolve into simple diagrams .
3 Years: Bones Shapes
During this phase, children begin to use basic shapes in their drawings as their fine motor command and hand-eye coordination ameliorate.
Shapes
Drawings at this age include the following shapes, combined in different ways:
- circles and squares
- crosses
- dots
- shapes that resemble letters T, Five and H
Drawing of a person
The beginning cartoon of a person usually emerges around 3 or 4 years of age.
These 'tadpole' people are drawn with just a head and usually legs direct attached to the caput.
Grip
A iii-year-old holds a pencil near the tip, betwixt the first two fingers and the thumb.
They utilise the preferred paw and concur the pencil with good control.
At this age, yous can help your kid develop a good tripod grasp by using triangular crayons.
Agreement
At this historic period, children are able to tell y'all what their scribbles represent, although you may not be able to see what they have described.
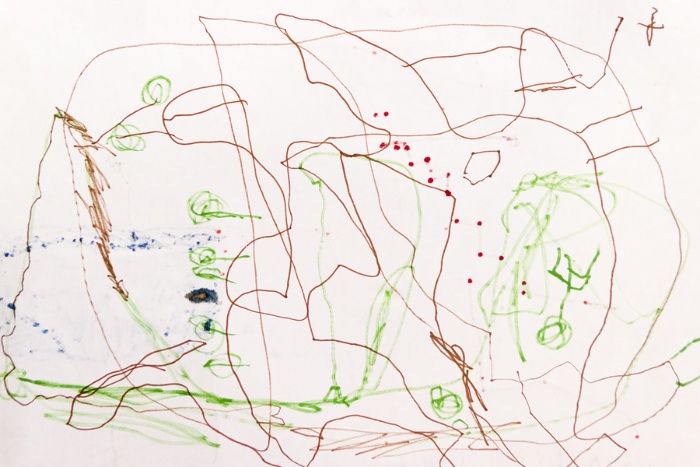


They usually name their picture while drawing information technology or after it is complete, but they do not start a drawing with a articulate plan for what they will depict.
The apply of colour at this phase is unrealistic and they ofttimes prefer to use only i color.
four Years: Patterns and 'Polliwog' People
By 4 years of age, patterns beginning emerging in children's drawings. A child will make a design and translate it as a representation of something, giving it a label.
Shapes
Their drawings include:
- Squares, circles and rectangles
- Attempts at triangles and diamonds, although she may non be able to form them yet
- Crosses
- Letters (pretend writing)
Drawing of a person
A 4-yr-old's drawing of a person volition progress from a head with legs to include details such as eyes – since eye contact is of import to them.
They draw non what they see, just what they know, and will add together details every bit they go of import to them.
Details such as arms, fingers and a trunk emerge.
Drawing other images
By 4-and-a-half they begin to combine two or more shapes or forms together to form basic images, such as a rectangle and a circle to class a hat. They often larn this from adults.
The beginning shapes children make consistently will usually grade people, but later on includes basic images such as a firm or sun.
Grip
At this phase, they hold a pencil with proficient control, in an adult fashion.
Understanding
Drawing takes on more meaning and intention. Children usually decide what they are going to describe earlier they begin.
They deliberately try to combine shapes and lines together and their pictures offset to await like the images they describe.
five Years: Pictures and Portraits
5-yr-olds begin to show much inventiveness in their drawings.
Shapes
Their drawings will include:
- Bones shapes
- Triangles and diamonds
- Spontaneous letters (to imitate writing)
Cartoon of a person
A portrait of a person emerges, with many details such as pilus, easily and fingers, feet and a body.
Drawing other images
They draw images such as animals, houses, vehicles, trees, plants, flowers and rainbows.
They are able to include details – such as cartoon a house with a door, windows, roof and chimney.

Grip
By v years of age, children should have developed practiced control when belongings a pencil, crayon or paintbrush.
Agreement
Children will now describe spontaneously and begin to prove their ain background, interests and experiences in their drawings. They depict what they know.
Their representation of people, animals and houses changes constantly.
They volition likewise proper name their motion-picture show before starting time.
They can colour inside the lines but their use of colour may still be unrealistic.
At this signal, people and objects may all the same be floating in the air as children are withal developing spatial perception.
They unremarkably place themself in the middle of a drawing due to their egoistic nature (seeing themselves as the centre of the world).
6 Years: Drawings Represent Interests and Experience
Past 6 or 7 years, children take their own style of drawing, which tin can ordinarily be recognized by adults.
Shapes
By the time they are seven, they will be able to grade good circles, squares, rectangles, triangles and diamonds in his drawings.
Drawing of a person
A kid commonly settles on a certain representation of a person at this age and tends to draw them all with the same basic shape.
For example, they will draw the whole family with the same body outline but will make the members of the family unit different sizes and show gender with hair and apparel.
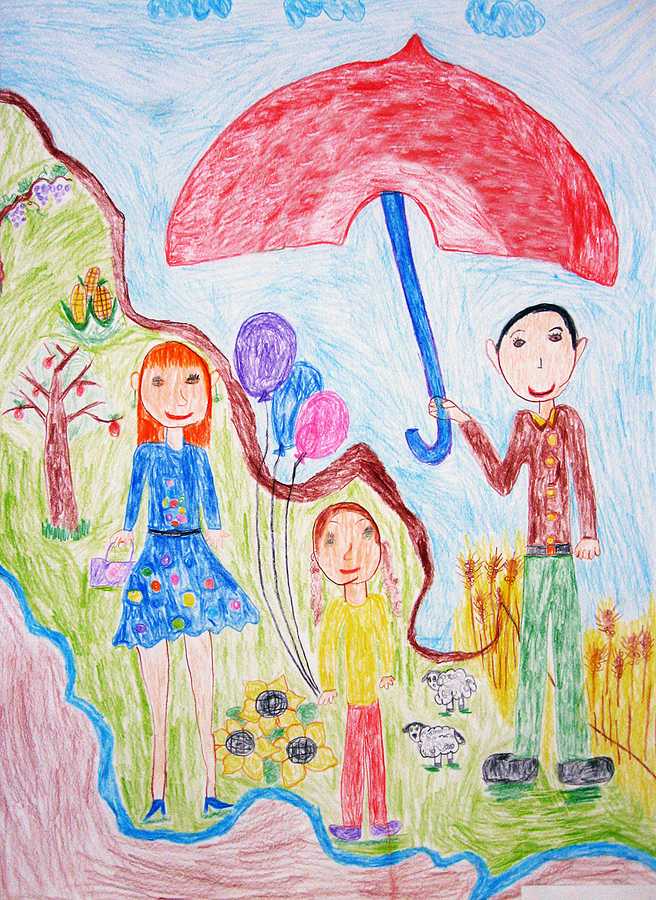
Drawing other images
Drawings stand for all kinds of animals and things, usually those that interest them the near.
They tend to draw animals with human-like faces.
Understanding
At this stage, children show their higher level of cognition by cartoon people, animals and objects on a baseline, such every bit on the footing or grass.

They also show perception by cartoon, for example, trees higher than the house or flowers that are small.
This drawing shows a child's greater understanding of depth and distance.

The way they see the world comes through their drawings. They leave out unimportant things and enlarges things that are important to them.
They may draw a small door on a business firm, just big plenty for themselves, or very high windows, since they cannot achieve them.
They tin can as well testify move in their drawings past portraying objects that are flying or drawing the legs of an animal wider apart if running.
Their use of colour becomes quite realistic.
I promise you've enjoyed reading about the stages of drawing development in young children and are inspired to encourage your children to practice lots of free drawing and creative expression.
Sources:
Hendrick, H . 1990. Full Learning: Developmental Curriculum for the Young Kid . Tertiary Edition. Macmillan Publishing Company: New York.
Pieterse, Chiliad. 2007. Language and School Readiness . Metz Printing: Welgemoed.
Natanson, J. 1998. Learning Through Play: A parent's guide to the first 5 years. Tafelberg Publishers Express: Cape Town.
Fisher, B. 1991. Joyful Learning: A Whole Language Kindergarten. Heinemann: New Hampshire.
Source: https://empoweredparents.co/child-development-drawing-stages/
Posted by: fostersagoonger.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Teach Kids To Draw People"
Post a Comment